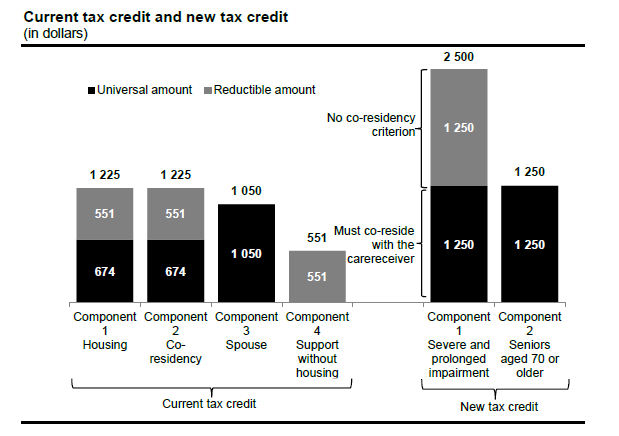
Starting in 2020, the four existing components of the tax credit for informal caregivers of persons of full age will be replaced by the new refundable tax credit, called the “tax credit for caregivers,” comprising the following two components:
- component 1: universal basic tax assistance of $1,250 (no co-residency requirement) for a caregiver providing care to a person aged 18 or older who has a severe and prolonged impairment and needs assistance in carrying out a basic activity of daily living;
- component 2: universal tax assistance of $1,250 for a caregiver who supports and co-resides with a relative aged 70 or older.
The following graph, from the Additional Information of the 2020-2021 Budget, illustrates the two components of the new credit.
Basic conditions
A caregiver can claim the refundable tax credit for caregivers if he or she meets all of the following conditions:
- the caregiver resided in Québec on December 31, 2020;
- the caregiver no remuneration for the assistance provided to the eligible carereceiver;
- no one, other than the caregiver’s spouse, is claiming an amount on line 367, 378 or 381 of their return with respect to the caregiver;
- no one is claiming an amount the tax credit for caregivers with respect to the caregiver;
- the caregiver or the spouse, where applicable, were not exempt from tax for 2020.
Eligible carereceiver:
- A person aged 18 or over and who has a severe and prolonged impairment in mental or physical functions might be:
- the caregiver’s spouse;
- the caregiver’s child, grandchild, nephew, niece, brother, sister or those of the caregiver’s spouse;
- the father, mother, grandfather, grandmother, uncle, aunt, great-uncle or great-aunt of the caregiver or of the caregiver’s spouse or any other direct ascendant of the caregiver or of the caregiver’s spouse;
- a person with no relationship with the caregiver, provided a certificate (Form TP-1029.AN.A) delivered by a health and social services professional certifies that the caregiver provides ongoing assistance to the carereceiver in carrying out a basic activity of daily living.
- a person aged 70 or over who has no impairment can be the father, mother, grandfather, grandmother, uncle, aunt, great-uncle or great-aunt of the caregiver or of the caregiver’s spouse or any other direct ascendant of the caregiver or of the caregiver’s spouse.
- the carereceiver must not live in a dwelling located in a seniors’ residence (see the definition on line 458) or in a facility of the public network.
Part A – Address of the dwelling
In Part A, indicate the address of the dwelling where the caregiver cohabited with the carereceiver(s) covered in Part B or D as well as the person(s) who owned, rented or sublet the dwelling.
Part B – Caregiver cohabiting with an adult person with an impairment
The caregiver might be eligible for a tax credit of $1,250 as well as an additional amount of up to $1,250 if the following conditions are met:
- the caregiver cared for an adult person with a severe and prolonged impairment in mental or physical functions;
- the caregiver cohabited with this person;
- the dwelling in which the caregiver and the carereceiver cohabited (see the definition in line 361) was owned, co-owned, rented, co-rented or sublet by the caregiver or the carereceiver (or the caregiver’s spouse or the carereceiver’s spouse if he or she lived with the caregiver);
- the cohabitation period lasted at least 365 consecutive days, 183 of which were in 2020.
Part C – Caregiver not cohabiting with an adult person with an impairment
The caregiver might be eligible for a tax credit of $1,250 if the following conditions are met:
- the caregiver cared for an adult person with a severe and prolonged impairment in mental or physical functions;
- the care period lasted at least 365 consecutive days, 183 of which were in 2020.
Part D – Caregiver cohabiting with a person (other than his or her spouse) aged 70 or over and who has no impairment
The caregiver might be eligible for a tax credit of $1,250 if the following conditions are met:
- the caregiver cohabited with a person (other than his or her spouse) aged 70 or over and who has no impairment;
- the dwelling in which the caregiver and the carereceiver cohabited (see the definition in line 361) was owned, co-owned, rented, co-rented or sublet by the caregiver or the carereceiver (or the caregiver’s spouse or the carereceiver’s spouse if he or she lived with the caregiver);
- the cohabitation period lasted at least 365 consecutive days, 183 of which were in 2020.
Note: For the application of the tax credit, the period of 365 consecutive days must have begun in 2019 or 2020. If it begun in 2020, it can end in 2021.
Particular case
If the carereceiver died in 2020, the caregiver must have cohabited with and care for him or her, as the case may be, for a period of at least 365 consecutive days following the date of death to be eligible for the 2020 tax credit.
Inability to live alone
The inability to live alone must be certified by a health professional, who must complete Part 3 of Form TP-752.0.14. If the person with an impairment unable to live alone and Form TP-752.0.14 has already been filed in a prior year in which Part 3 was not completed, the form must be filed again.
If the spouse’s or the carereceiver’s income tax return is paper-filed, Form TP-752.0.14 must be mailed to Revenu Québec to the address corresponding to the spouse’s or eligible relative’s region. If the spouse’s or the carereceiver’s income tax return is filed electronically, the form must be mailed to the NetFile Québec Help Centre at the following address:
Direction principale des relations avec la clientèle des particuliers
Revenu Québec
C. P. 3000, succursale Place-Desjardins
Montréal QC H5B 1A4
See Also